Comms & Security Privacy vs. Dignity
Australia, like many countries around the world, has sought to respond to the critical need to have cyber capabilities. This, is about that.

Source: MarkLogic Semantic Graph Developers Guide
When defining social patterns that seek to attend to security needs, there is a multitude of factors that should be taken into consideration.
Source: WIkiPedia
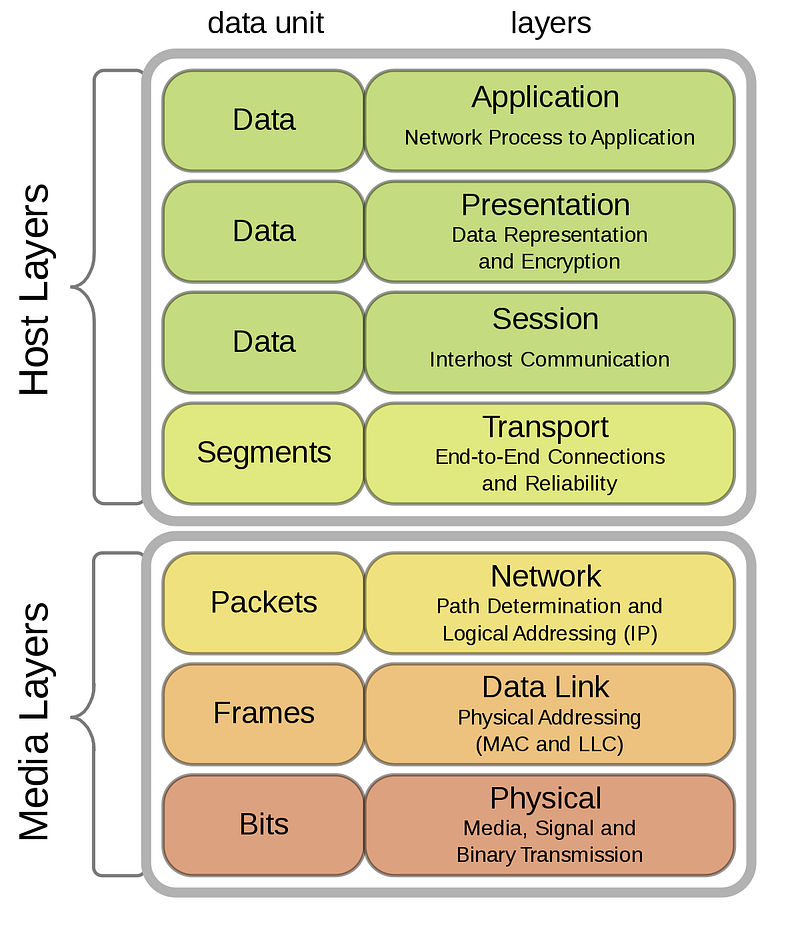
The OSI Model
The OSI Model is used to describe the various layers involved in electronic communications systems.
At the very top is the application layer, which is the webpage itself. At the very bottom, is the physical media layer, the cable or transmission method.
When considering approaches to security; experts bring into their considerations attack-vector opportunities that can be made at any of these levels.
There is a wide-spread false belief in concepts such as anonymity and the fable that systems can be cheaply designed and used to provide 100% security. Whilst this series of false beliefs makes it easier to catch crooks, it is in-fact based upon a series of falsehoods, which in-turn have ripple effects across community & how we talk about real world problems.
A Laser Surveillance Example
For instance; an ‘end-to-end’ encrypted communications application, may provide ‘security’ between end-points; but that doesn’t mean the intended purpose of those communications interactions between two agents cannot be intercepted at the endpoint, in relation to the person or the device.
The pragmatic reality is; the concept of security should be employed in relation to a set of identified considerations that in-turn relate to the definition statement of what is sought to be achieved.
There are an array of means to identify and define both social-informatics, supported biometrics, alongside an array of means through which biometrics can be applied, in complex systems, to perform complex tasks; offering users, extraordinary capabilities. The blending method, is a tactical capability, art. Yet the practical employment of it, can often lead to unintended outcomes as a consequence of how solutions are defined; what is ‘in scope’ and what is not.
Source: Flickr — similar to Time|Quality|Money
Security for one agent, may mean insecurity for another.
Misguided targeting of the wrong actor, may assist crime.
When defining systems that are intended to be depended upon by societies, proper evaluation becomes increasingly important for socioeconomic health.
Why a Human Centric Web would yield better security capabilities.
An array of considerations that seek to improve methods to deliver a series of seemingly intended outcomes; for security techniques that include considerations relating to the following objective qualities,
- KYC / KYCC — Know Your Customer, Know Your Customers, Customer.
- Privacy Preserving as a constituent object part to the preservation of dignity.
- Provenance, Rule of Law & Social Equity, Procedural Fairness & Intelligence
- Cyber warfare ready, informatics art and tactical capabilities
- Safety & Sovereign (domestic) Governance Capabilities.
- International trade and social participation; on just terms.
I’ll try to illustrate a few thoughts about each of these aspects, and in-turn relate my considerations back to the strategies employed in my other articles.
1. KYC / KYCC
Know Your Customer & Know Your Customers Customer; are terms that are most-often used in relation to, online systems, that are connected to means for financial transactions (online). The practical employment of KYC/KYCC, lives within, the context of what is added to this concept as ‘anti-money laundering’ (AML); which in-effect means, the ability to identify criminal activities; and, be equipped to do something about it. Without being able to identify the parties involved; it would be impossible to do so and so KYC/AML.
KYC/KYCC is often an over-simplified activity set; whilst best endeavours are made to adequately respond to the complex set of problems, for specified purposes.
Law enforcement and state authorities need to be able to maintain their responsibilities on behalf of societies to keep them safe.
Another part of the problem, is that people independently have the right to be safe, and if state authorities refuse to act; have a right to take a matter to court and/or seek other legal means of recourse as to retain their right to be safe.
This is not well supported by systems designed to solely support KYC/AML
There are many ways ‘digital identity’ can be achieved; and similar to a 100 point check, the more (reliable) data points that can be made, the better.
Yet, therein — there are many more devils, in the detail.
Many of the instruments that can be used to perform KYC functions, are provided by overseas providers. Consequentially, requests need to be sent with supportive policies between governments; to & from the ‘data custodian’, which in-turn forms a ripple effect on capacities relating to, terms of trade.
As is demonstrated by the presentation materials provided in the above OpenLink Virtuoso presentation; there is a means technically, to collate records obtained from various providers and unify these records into a graph.
But this can only be done lawfully & in a manner that is technically supported.
The above illustration is useful for a couple of reasons. Firstly, it illustrates a meme that illustrates the human factors relating to users.
Secondly, without being the intended purpose of it; it also demonstrates the issue that whilst one person is the user, there may be another in the background eliciting an act to be carried out by the inferred “user”, who can in-turn be used.
The distinction made between KYC and KYCC makes an attempt to respond to these sorts of issues by forming a tooling related mindset to graph complexity.
But the way business systems have been deployed world-wide today, makes this objective requirement harder to achieve; as is dependent upon nationality, in a complex social graph.
The Debate about Cryptographic Instruments
To illustrate one of the many issues that relates to this; Internet Society recently published an article stating: “The Internet Society’s Concerns on the Recent Government Action in Kazakhstan Regarding Encrypted Internet Traffic”. Certificate infrastructure is an instrumental set of tools for Internet.
The internet society is a core tenant to internet governance worldwide.
In their article, they speak of their concerns that the Root Certificate could be used to; facilitate,
‘means that the government could see, monitor, record, and even block interactions between Kazakh users and any website, including banks, email providers, social networks — and critical public services like electricity, elections, hospitals, and transportation.’
To put this in perspective; device operating systems and applications such as Web Browsers package with them a specified group of root key certificates with their products. To illustrate the point, here’s the post about OSX & Mozilla.
The difference between installing a root-key certificate and not needing to do so, get down to whether or not the certificate chain is already supported. Whilst many countries have local root-key infrastructure packaged with these products; there are also many countries that do not.
It is often the case that Universities and other enterprise environments install certificate infrastructure on employee (or student) devices to connect them to their networks.
This underlying consideration is one of the most instrumental components to how ‘content security’ on the internet is made to work. Tools like TLS provides the ability to encrypt data between a consumer device and the service provider.
Where the service provider is overseas, this means the ability to identify information relating to an event in-turn requires a request to the O/S Company. The generic statement used as to why this is reasonably (as is associated to harmful events both in civil and criminal contexts); is that, the tools are of instrumental importance to preserve security & privacy.
Whilst privacy, when employed for proper purpose; is of upmost importance,
Privacy, is in-turn used to support institutional interests as does in-turn relate to the service providers jurisdictional context, as stipulated by the Choice of Law Clause used in the terms of service contracts; used both for citizens and aliens.
The implications of these procedural infrastructure frameworks, have impacts across many levels of societies, economies incorporating the trade, security & sovereignty supporting infrastructure required by participating entities.
This is in-turn coupled with domestic infrastructure practices that relate identifiers that support forensics to service providers or companies; not people (natural persons), which is in-turn coupled with the above issue.
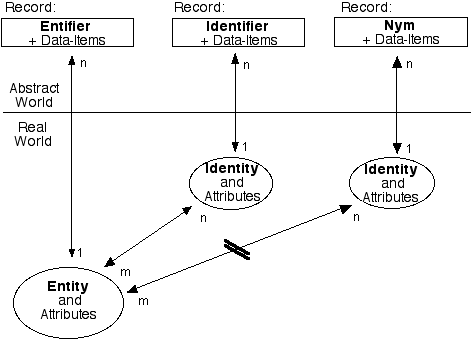
Source: Roger Clarke, A Sufficiently Rich Model of (Id)entity, Authentication and Authorisation 2010
The image displayed is by Roger Clarke whereby; he illustrates some of the complexities involved in defining human (digital) identity models. Roger is one of few (2, i think) who have been awarded the Australian Privacy Medal.
When considering the problem in simple terms; Human identity is now considered to be a ‘content problem’ from a perspective of how Internet, is made to work. The business systems, have been produced to support trade, between companies / groups; without tooling to support extensions for human agency.
Internet evolved as a consequence of TCP/IP.
Whilst the first version is still mostly used today (IPv4) this was considered by its co-inventor to have been a ‘pre-release’ and unfinished project that got our into the wild; and so, IPv6 was produced, making an array of important changes including those relating to security.
As IPv4 had a limitation on the number of addresses, ISPs often used NAT. IPv6 attended to many of the underlying factors causing this to occur. IPv6 also introduced a suite of security capabilities at the protocol layer, that was not able to be performed on networks that made use of IPv4.
Part of the IPv6 spec, security tools such as DNSSEC and DANE make use of certificate infrastructure to support security tooling at the protocol level.
These tools can be used with others to form more complex security models. As an example, public keys could be published in DNS for use with applications.
But the internet protocol identifiers; IP Addresses (and subnets) aren’t allocated to users, rather, their allocated to providers — or companies.
“IPv6 is a topological identifier and should NOT be used as a logical one.”
source: Vint Cerf, via email. 31st October 2013
As defined by current practices governed via IANA; the way IP addresses are managed is that a service provider will make a request to be allocated a number-range; and they in-turn make use of this allocation to provide numbers (dynamically) to end-points, or end-user (devices).
This means, in-effect, the number range is provided by way of contract law to a company who are in-turn legally provided the beneficial use of them. These commercial arrangements are not able to be obtained easily by citizens.
Therein, it’s a bit like a system that says any home address, must be owned by a company and not by a person. Whilst human identity was rendered agency in the physical world when internet was first invented, this is now changing, rapidly.
In circumstances of Law Enforcement related purposes; If a request needs to be made to identify a person associated with one of these numbers; the request is made by a authorised agency, generally on a domestic basis; to the ISP (internet Service Provider) or OSP (Online Service Provider); and the provider is then obligated get the data, and provides the information to the law enforcement agency. If a law enforcement agency isn’t interested; or if its a “civil matter”, that doesn’t really work, indeed generally; it doesn’t apply.
Apparently, it’s prohibitively expensive to do, so often its not done at all.
Unlike the ease of seeking police attendance if someone is physically threatening, seeking to cause harm or injury to a person; online, it seemingly doesn’t matter.
Yet, to understand why; as i’ve otherwise illustrated in my other ‘human centric web’ related works; one needs to consider how it was that human beings were paid to support their lives, whilst making cyber policy decisions.
The way laws have been made to support internet; have not incorporated funding or capability support to properly discern the needs of the civil tenant. Whilst Service Providers, Law Enforcement and other persona ficta groups have had; both, the mandate to operationally support time-consuming and complex works, to evaluate what the needs of their employer (the organisation) is; and, the funding to pay for their work and safety / security needs whilst doing so,
the needs of civilians are largely left ‘out of scope’ as no voices of support were in the room and those that were, have insufficient funding as to be able to stay safe and do to proper effect, the important job that is required of someone, to do.
Consequentially; As a result,
The most troubling issues relate to those where a commercial conflict of interest exists between basic aspects of human agency and freedoms; vs the opportunity to make money for a subscription service; whilst employees & stakeholders, sleep.
Certificate infrastructure is used to support an array of ‘verifiable claims’.
The types of verifiable claims, that all use cryptography, is expanding. Cryptography is of intrinsic importance to the function of the cyber domain, yet the suggestion that sovereign nations should not support locally their own independent infrastructure services; seems to be, at best, misleading.
Whilst it is not cheap to operate crypto capabilities, it may be far more expensive not to do so. Therein, part of the problem is that it’s hard to know, unless its addressed in the first place. Business systems are the means through which agreements are made that serve the purpose of actions otherwise employed by way of attacking vulnerabilities embodied within technical infrastructure.
If trade between nations provides the right to share knowledge; no need for “hacking”, or ‘false labelling’ as to describe systems said to be ‘secure’ but are not.
The vast majority of KYCC related services are now reduced to a subset of otherwise available tools; whereby, direct commercial relationships between institutions of trust and ‘consumers’ is used to traverse the (engendered, business systems) gap; not based on how ‘knowledge resources’ are created, but rather how money is distributed between parties, doing deals.
In Effect; the use of these methods are moreover employed for the purposes of ensuring an insurable approach on behalf of institutional stakeholders; with little regard more broadly, to the needs of natural persons; or so is the case, at present.
Considerations i have tried to canvas above; inform suggestions such as,
a. It’s kinda important for nations to support local root-cert infrastructure.
b. cryptography is in-turn important for securing an array of other infrastructure. This infrastructure relates both to the ‘internet layers’ (being the data communications infrastructure) in addition to the semantic layers; or informatics systems, used for important tasks socioeconomically, everywhere.
c. Whilst KYC/KYCC is really important; not everyone needs to know everything. Where ‘inspection’ is required for lawful purpose, that capability should be provided domestically, in an economically defined & accessible manner.
d. International support is required and will always be required. Yet the demands put upon KYC/KYCC infrastructure is going to grow rapidly.
For example:
Libra has recently announced plans to support UN Sustainability goals such as 16.9 (unbanked) in their efforts to deliver a payment solution; that others have failed to do, even though the type of ideas presented are indeed very old.
One of the many problems with their idea of providing both economic and identity services, from afar, to the unbanked without local policing; it may lead to new forms of human exploitation; as to facilitate crime, in emergent & new ways.
Yet conversely, facebook and few others now have the global graph infrastructure capabilities that may in-turn be best able to identify emergent & harmful, issues.
The other issue highlighted by banking experts working in the targeted regions is that the majority of financial transactions are carried out using cash. As a consequence, libra may be locally controlled by those ‘cash in’, ‘cash-out’ service providers (NB: BankServAfrica)
A Fast Fact: International Companies, do not better support personhood than good domestic governments. Related legal framework ecosystems, materially (as distinct to ideologically) support principles such as rule of law.
Historical examples of cases where this type of infrastructure was not in-place, is often closely linked to those of slavery, exploitation & human misery.
2. Privacy Preserving (nonsense) vs. Dignity preserving civil service Intents.
When human rights advocates engage in the topical conversation of privacy, the broader intent of their advocacy, and prosecutorial activities, is towards the interests of persons and their societies; which are generally well intended.
Yet for reasons that are complex — this is now, all too often, perverted or made mute.
Sadly, there is a disproportionate, volumetric relationship that can be graphed (best by US infrastructure services); of influences brought about by US Policy and US domestic law.
Such factors as; corporate personhood, which is now also reflected in the authorship of laws elsewhere; including but not exclusive to Australia, when linked to global ICT vendor strategies, impacts our way of life and our means to participate and be involved, in important decisions.
What many may know, or be easily provided the opportunity to test; is the object and considered, derivative legislation, that has sought to address critical issues, that are now made far less than clear.
The vast majority of databases storing information about persons, that is intended to directly infer decision making support for dealings with persons, are stored by companies; some local, but many also internationally. Should the person seek a copy of that information about them, the process is made very hard.
Privacy Law is now employed all too often to protect corporate needs; that include but are not limited to, insurable risk and accumulation & commercial use of knowledge based capital; or purported knowledge capital, in the case of fictions; where intent is prosecuted for profit, by seeking to restrict access to records and the means to support and fulfil, proper audits.
It is the case today, that in all too many circumstances, companies claim they are unable to share information they store about a person with that person, for reasons that are stated to be of privacy concerns or considerations. Whilst some jurisdictions have tried to address this (without upsetting the apple cart as to meaningfully disaffect, international knowledge capital asset holders); the outcomes don’t really do much good, for humanity.
Further barriers are built upon this cyber first landscape of informatics policy infrastructure; leading to significant ‘data quality’ issues, which negatively impact persons.
Whilst the idea of websites providing APIs is very well known, the use of those APIs with Human Beings is generally, expressly, as to be consumed. The nature of services generally seek to leverage strategies similar to older traditions of golden handcuffs, so that your service provider becomes an instrumental and no-longer-optional part of your life, clipping the ticket (obtaining a % of their earnings) along the way… generally, for corporate profits, or to protect against accountability related issues (ie: exposing malfeasance causing injury). This isn’t a technically determination…
The distinction between these forms of ‘privacy preserving’ principles and those of ‘dignity preserving’ principles, gets to the heart of intended purposes. Or perhaps type of heart, as one relates to things that are easily sold, that in-turn requires continual upkeep by way of paid services; and the other, needs kindness to heal.
Whilst “misleading and deceptive conduct”, may be one of many behaviours that act to influence causality; that law enforcement officials are known consider to be a ‘stock in trade’; judged only if systems lead to getting caught,
If systems are designed to ensure tools, are in control of natural world actors, rather than the other way around; then, the difference between fiction and non-fiction doesn’t matter any more, as the decision in-turn discreetly infers.
Whereby; the confluence of tooling incorporates legal constructs; including contracts, laws and corporations; in addition to the tools beneficially operated for their needs, which in-turn leads to an influence of social culture; the problem from a security perspective is; that issues built-into the systems, in-turn cause an array of insecurities in the real-world. Informatics governance principles, that are built upon poor foundations, support insecurity, unsafely.
The impossibility of perfection; other than as it is, in the real-world
If in reality; 100% secure, in-fact means; something does not exist at all; then logically, what evolves, are considerations about ‘sense making’, built into systems, that seek to offer a set of characteristics that can be made use of, in an ‘as intended’ systemic solutions.
Technical Solution needs supporting infrastructure in the real-world.
As such; Improvements to ‘security services design’ are made more secure when built upon principles of accountability, in addition to obfuscation. Both concepts are coupled & useful constituent component for the design of reliable and secure, operational cyber-physical systems frameworks.
Inclusive Social Informatics
Increasingly theres a means to support social informatics and related inferencing capabilities. Currently they’re considered instrumental for the functional support of enterprise systems, such as search, advertising and social network platforms as well as AI Assistants and many other commercial services. As a consequence of ‘security design’ these systems today, can often provide a clearer picture of persons & situations; than is able to be employed by those who are sworn by law to protect the real-world person.
The failings of todays strategic design of informatics; does not meaningfully make accessibly available, functional capacities for the ‘data subject’ (person) to inspect or make use of these cyber-physical systems, as to clarify a dispute, resource safety or resolve issues that may disaffect their lives and those of others; by making use of these systems (particularly those funded by taxpayers) to tender real-world facts for consideration, in a court of law.
The circumstance may be considered today consistent with ‘privacy preserving’ principles; whilst knowingly likely to fail reasonable dignity preserving tests.
The considerations illustrated thereafter consider; aspects in society such as,
a. there’s alot of money spent protecting fundamental wrongdoing in a manner that’s making meaningful utility of privacy, amongst other things.
This is an intrinsically important constituent object; and commonplace practice, leading to enormous funds, being put to morally bankrupt, use.
The problem appears to be that we’re all now ‘trapped in the system’, and to fix those characteristics; we need to redesign how the system is made to work.
Whilst it may be the case that short-term economic advantages leads to systemic growth of an issue; what seemingly happens overtime is that those issues become sufficiently well known, as to be effectively communicated in a format that leads to some form of enquiry, such as a royal commission. Thereafter, economically speaking, those who are harmed whilst having done the right thing as a participant in a broken system; whilst retaining moral equity, continue to be made the fools at their expense; whilst others, who are better able to act in professional practices as liars, modify how they do it.
Some of these attributes relating to success are built in to people. So what sort of characteristics about people do we want to most encourage, for Security?
Security capabilities should want to ensure their capacities are able to discern fact from fiction; issues left (and funded) to fester; engender other issues (that can be correlated in graphs) harming safety. Dealing with issues associated to harms committed upon civilians may be inconvenient; but leaders getting told about it overseas as to influence terms of trade, would seemingly be worse (but potentially also, easily kept secret).
Secrecy =! Security, and privacy as used today, is a poor cousin to dignity enhancing alternatives. If a civilian visits a gynaecologist, it may influence what is presented to them on the web. Whilst confidentiality is an important part of any dignity enhancing approach, as one wouldn’t want a gynaecologist to be instagram’ing their visitors; reality is, the policy architecture is all messed up. If cyber security is going to triage issues of real-world safety, the policies today that poorly serves all involved, under the banner of privacy, could be reviewed through the lens of a dignity enhancing approach. Preserving privacy, but not at the expense of reality, as to engender fiction.
b. ripple effects across industry.
People make assumptions based upon their ‘view’ of others; which incorporate from a human psychological point of view, an array of discriminating factors, many that relate to the conceptual attributions notated by association to a person who is considered to be ‘successful’ or a ‘success’ (ie: money, wealth, assets, knowledge, ethically attributable behaviours).
Where false informatics frameworks are employed as a useful interference tool with consequential social implications engendered via cyber infrastructure; its not best able to be employed to support insurable risk, or fit & proper hygiene. We operate in an international marketplace, our capacity to identify and make best use of our natural resources (inc. people) is important.
c. Good Hygiene; starts with means to protect and serve human dignity.
To achieve this; we need to better consider how and why dignity features so prominently in the UDHR, and built tools that better equip societies to make use of the social-informatics that are defined by people for themselves, in a manner that is protected by law; making use of, some set of legal principles.
3. Provenance, Rule of Law & Social Equity, Procedural Fairness & Intelligence
As a consequence of social factors; that include but are not limited to, aspects express and implicit to aspect considerations prefaced in points (1) & (2);
The ability to adequately perform ‘sense making’ activities is significantly hampered in an enumerate number of ways. As is a constituent force, correlated to these problems, the ability to support provenance is made difficult. As a consequence also, aspects relating to ‘rule of law’ are relatively thrown out the window.
- Social equity suffers,
- procedural fairness undermined; and,
whilst intelligence may seek to build cases, upon ‘fake news’; that isn’t really going to help long-term, other than may be associated to a few ‘news’ spots.
One might consider an alternative point of view,
If systems are designed not to work, then the continued foundation of seeking to use the argument, that relevant organisations ‘do not have enough funding to do their job better’, becomes a continuum for money to be sent into the void.
One way to address what might be an enormously inconvenient problem; perhaps as a safer path, would be to engender a policy that effectively revoked the role of citizen as an easier path, to that of ensured procedural fairness. by employing all as Government employees, protections would be made available via employment terms; whereby any problems becomes one of administration internally, rather more complex stakeholder considerations; requiring consideration of the impacts nonsense pervasively delivers, to distorts and disorientate the means for others to act.
The role of Government is about, public service — for those who are not employed by gov in particular, who for reasons of life, seek their help. As has been well publicised in Australian Press, activities of social security today, in one program alone has been attributed to thousands of deaths. Security is now sought from the people, as to protect something other than people, as the people see impacts upon others, in reality, without any means to do anything meaningful about it..
In order to have any system capable of delivering the materially useful tooling, as required for any ‘fit and proper’, morally appropriate, law enforcement and cyber-security capability; the essential the role of citizens, as impacted by cyber-physical systems digitally, really needs to be addressed.
by addressing the issue of ‘digital citizenship’ or moreover — personhood, as it relates to dynamic influences of cyber activities and repercussive actualities; the means to more than simply provide an ability for employees of 3rd parties to tender a definition of others, to the exclusion of any human agency; as is required of them, through the lens of their job role, sometimes in secret, as to be protected by institutionally operated ‘privacy’ systems; impacts everyone, indiscriminately — yet, in a variety of different ways.
SOCIAL FACTORS
If infrastructure were modernised; as to support sovereign capabilities that are designed to equip a domestic state governance environment, to support local moral principles; as embodied by the spirit of the law, and such principles as ‘rule of law’, but not solely,
Then there is a need to consider whether, how & who; in relation to what terms, may the full-force of technological capabilities be brought to bare, in a timely manner; as to bring a direct and immediate response to malfeasances and other forms of wrong-doing. Forming strategies for ‘insurable risk’ by obfuscating the existence or nature of a problem; is not a useful component to any practical utility of intelligence; and/or, the means to engender, or make use of wisdom embodied as a core part of who we are as homo sapiens.
As may be considered meaningfully important for any curated set of actions, capable of acceptance; in a court of law, cyber can be used to rewrite the definition of how any system of democracy is made to function. This can be used to undermine old rules built pre-internet; or it can be used to help us evolve. Either way, actions will present a series of traits that will illustrate themselves as components of invested infrastructure, of instrumental importance in the creation and operation of any approach; secure or insecure.
Relationships of safety are not built upon the means for one, to consume another…
Without the means to properly present the complex nature of a situation to those in society responsible to judge and protect fairness; society as we know it is lost. The intrinsic effects transit across economic policies and process, leading to implications about how things are done today; and the costs involved in redesigning cyber-physical systems as to amend bad policy, solve problems and build improved alternatives that grow to yield better outcomes.
There are many examples in past of slavery, today ICT can be employed to enslave the populations of entire countries, simply using — cyber tooling. The implication is not unlike that of old production practices employing slavery. Whilst web Slavery, doesn’t require the trader to acknowledge the work of the enslaved; nor finance or support the cost of their living expenses, the problem is similar to the older versions that did; in that, labour without slavery, may be considered an inconvenient expense. So provenance, can be inconvenient, particularly when there’s a lack of economic & security tools to support trade in relation to an activity governance framework that values what people do.
The problem about not doing so; is that security problems / gaps, get built in.
The inference made therein;
a. If the data about people is being stored in connection to that person; then the ability to forensically track and figure out what’s going on, is better able to be facilitated lawfully on a domestic basis, rather than simply leaving all that stuff about reality somewhere, anywhere, lots of places — overseas.
policies to support “sense making” cyber-legal-physical systems, should incorporate considerations for the need of citizens; without that, other systemic tenants are not able to (lawfully) be equipped to do the same.
This gets to the heart of ‘digital twin’ considerations, across all spectrums.
If we actually care about reality; and seek to build civil / societal infrastructure that is designed to support it, in reality, as a non-fiction activity, rather than any alternative fiction engineering concept for useful acquisition of government expenditure; then,
its kinda important to understand that there is an instrumental link between granting forensic means of discovery and beneficial socioeconomic utility to civilians; as a means to, also render meaningful benefit for security & intelligence capabilities, than to reject the consideration, as an inconvenience. If government has no department or office to equip its civilians, it should make one. Yet the practice of sending queries across multiple departments, without practically considering an approach to solve problems, won’t work.
I am not here to suggest government should necessarily operate it all; or indeed that the only employer in future, should be government; rather,
Whilst it might be hard to consider why the means to make use of critical online tooling to better participate in our system of government; with our elected representatives and such; is a good thing, it’s moreover instrumental.
The ability to misuse systems that were never designed to support contingents of the civil tenant seeking to be good actors; is best exploited by those who wilfully seek to do bad things, for the purpose of profits.
In Reality; activities of work by human beings, are attributable to costs. For some reason on the internet today, in this ‘secure’ system, it’s not. This is one of many insecurities that have been built into the systems, that is now leading to an array of very negative effects. Will those whose actions led to robodebt killing thousands, for profits, lead to them being known for doing so? no. that would be inconvenient; but from a security perspective, what were they taught, was the best way for them, to go about being ‘successful’ as a person?
What was it they said in a job interview, when fact is, others didn’t get the job.
4. Cyber warfare ready, informatics art and tactical capabilities
The importance of being properly equipped on a domestic level, as to support the needs of domestic geographical regions; at times of disaster, whether natural or man-made; requires in-turn, trusted & reliable cyber capabilities.
Building sandcastles on fiction, isn’t going to help solve non-fiction issues in the real-world.. Indeed also, the intent of seeking to rely upon fiction, can be weaponised by sophisticated & organised crime, undermining other capabilities.
As i have described in my other articles (as noted below), there’s a capacity to make use of distributed / decentralised graph infrastructure; to make secure all sorts of things; connecting relationships between artifacts and people.
This is in-turn able to be contextualised; by known social variables, such as poverty, or social roles and the influence reality has on real-circumstances.
Considerations there somewhat try to illustrate something that can help better answer scenario related questions; like,
So, Australia is cut-off from the rest of the world; and some of the critical components of our technology infrastructure locally, have been made non-functional. What happens next…
5. Safety & Sovereign (domestic) Governance Capabilities.
If need to have domestic & democratically curated capabilities in Australia. They underpin our ability to maintain safety and civil order, alongside the provision of instrumental tools necessary to form supportive and defensible socioeconomic structures for trusted and reliable sovereign activity.
What this in-fact means is that we need to build local systems that employ the otherwise international capabilities of global, social graphs.
Except from: re:publica 2012 — Eben Moglen — Freedom of Thought Requires Free Media
The implications of the somewhat exceptional presentation by Eben Moglen in 2012 does not merely implicate issues put upon US Citizens, but moreover humanity — right across the world, the citizens of many countries, termed Aliens.
Sovereignty and citizenship are coupled on a inter-domestic basis; not an international basis. Henry Story’s works From Digital Sovereignty to the Web of Nations brings considerations to how the inter-webs can be thought out.
Without the apparatus required to continually support the meaningful utility of these core principles, undermines the whole.
It seems that the inferred situation today, brings about the consideration that the core tenants to how citizenship is meaningful in the real-world; now needs to be reviewed as to form a social contract for cyber; and how, ‘nation building programs’ formally associated to roads, bridges and other physical infrastructure, should now infer the need to do the same in the cyber domain.
How is anyone able to be safe, if who they are is defined solely in the information systems dynamically resourced as an asset of others…
The inference i am suggesting herein; is that, it’s important to ensure people are provided the means to protect their own safety & welfare; alongside the means for them to materially assist their children, and loved-ones.
Current systems, do not do this; as this form of functionality has been considered to be ‘out of scope’.
Consequentially, the emergent series of now critical problems; leads to billions in misappropriated expenditure, delivering both bad outcomes; and resourcing the defence of why purposeful & organised activities that did so, should be awarded economic benefits with impunity, for knowingly doing so.
The problem is, that this leads to human misery alongside other costly factors undermining our capacities to support and maintain socioeconomic security,
in reality; as is distinct to the outcomes formed through a one sided argument.
Our economic systems do not work if money made to be a limitless resource. It therefore matter, from a security perspective, how those funds are used.
Increasingly, companies and their agents; where there are efforts underway now to include artificial intelligence (software agents) are granted impunity.
Humanity, on the other side of the equastion, in reality, are not.
6. International trade and social participation; on just terms.
It is seemingly considered reasonable today; that people throughout the world who are actors in a competitive marketplace; consider unfair practices as a mainstay of capitalism, as to incorporate the use of intellectual property, contracts, international & domestic laws; asymmetrically, unto law.

source: visual capitalist
If a user disagrees with something in the ‘terms of service’ for a popular website they’ve got two options; agree or be excluded (from society, in-effect).
The idea that leaders in one country seek to best support the means for those in foreign regions to most gain economic, beneficial custodianship or ownership; over instrumental works of importance for the future of societies, economies & STEM is a fiction. Yet this is what we’re told, all constantly.
For the most part, such a practice may be considered unpatriotic, to do so.
So we’re sold ‘free’, and now we do not have low-cost domestic means, to domestically support R&D; which i’d suggest, has some sort of consequential impact across a multitude of spheres; relating to international ‘terms of trade’.
Whether it be the formation of terms to produce and consume natural world resources (including humans); or derivative works produce in relation to it.
The best outcome from an (international) acquirer is to get resources, for free. Better yet, if business systems can get international people to pay the acquirer as to provide the opportunity to take from them, resources for free, even better.
Or is it?
The sorts of things that need to be addressed are more than simply ‘taxation’. intertwined are the means to engage in trade with others; on fair terms, as is one constituent objective purpose that is at stake; the other, is meaningful (human) progress; in any manner that can materially benefit our ecosphere.
Security infrastructure, if it were better considered ‘from the ground up’, certainly involves technical considerations; but that’s not just about hacking a pipe that’s otherwise funnelling the beneficial utility of IP & Money, overseas.
Our capacity to produce and make meaningful utility of sense making apparatus on a domestic basis; is of enormous importance. Without it, we’re less able to add value other than as a raw resource, similar to meat and potatoes or lumber and minerals. I think, my works (with a handful of others) on ecosystems; can and would, resolve more useful outcomes. I think the means to better associate and make use of ‘social graph’ infrastructure, by law lawfully — is of importance; but not, as an Australian in the USA; rather, here.
Or in the UK, or moreover; wherever it is that a person might live, in the world. To do otherwise, is kinda like suggesting a person be sent to hell on the basis of what book, written in local language, be the, determining factor.
Conversely, the problematic causes also form issues surrounding; how and upon what terms, is should reasonably be expected that vulnerable Australians trust, their local government to ‘have their back’ and if this is not the case; what sorts of (wrongful) behaviours are undertaken by others, as to not be vulnerable to harms considered reasonably put upon the poor.
Where our investment into the Australian Creative sector, is now so under resourced, companies like facebook offer new solutions, from the USA.
So whilst the idea of going to another country and offering to freely provide the service of taking from them their oil reserves at no cost; is now known to be a bad deal, indeed one that wasn’t done even decades ago; that’s kinda what’s happening on the internet, as a few, seemingly enjoy the outcomes.
So, Cyber Security, in real-terms — is much more than the relatively simple needs of Cyber, and its really quite important this now be better considered.
Perhaps indirectly, what is less considered; is that if Australians get the infrastructure they need to better perform ‘in good faith’, so will Cyber.
Social Encryption: Social Informatics as a security Infrastructure toolset.
The implication of building decentralised social-infrastructure that makes use of cryptography and related trusted marks, such as time-stamps; is that the collation of information from across the network, becomes much more difficult to tamper with without leaving any traces; than is the case in centrally governed informatics systems & environments. As such, should an actor seek to change the informatics produced in relation to a particular event or incident; the networked infrastructure can be used, to make it difficult to achieve.
Whilst there are a number of valid use-cases that should reasonably be considered as to be incorporated into a supported feature set; the methodology to employ those tools would rely upon human centred actions.